
By
Raphael Santos
September 19, 2023
Updated
September 25, 2024
Artificial intelligence (AI) business usage has seen a vast increase across all industries over the past few years
Management in business sectors such as manufacturing, transport, finance, and medicine are investing in artificial intelligence in order to develop a competitive edge.
The use cases range from automating their activities, forecasting demand and enhancing the decision-making process.
Artificial intelligence is rapidly gaining acceptance worldwide, with businesses looking to leverage its potential to disrupt industries.
The bar chart below offers a comparison of global CEOs and CMOs regarding their companies' adoption levels of AI as of 2023. It’s clear from the data that AI has been widely accepted and integrated at various levels within businesses.
A notable 32% of CEOs report having already implemented AI into their operations, signaling a robust commitment to leveraging technology for operational advantage.
Meanwhile, 23% of CEOs have plans to adopt AI across all business units immediately, compared to 6% of CMOs, which could suggest either a difference in strategic priorities or a variance in the perception of AI's immediate applicability in marketing functions.
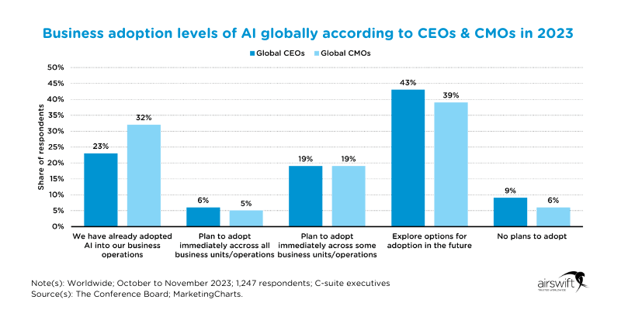
In addition, exploration of AI options for future adoption is significantly higher among CMOs (43%) compared to CEOs (19%), perhaps reflecting a more cautious or exploratory approach within the marketing domain, or a phased strategy aligned with customer engagement metrics and marketing technologies.
So, as AI continues to make waves across industries, let's delve deeper into its impact and the exciting opportunities it presents for enhancing business processes. Check out how artificial intelligence is revolutionizing various sectors:
Examples of industries using AI
 Oil and gas
Oil and gas
The oil and gas industry has seen a fair amount of turbulence over the last few years. However, as oil prices increase, employees in the industry are certainly on firmer ground.
However, the prospect of new digital trends presents a challenge for oil and gas. Doing so is key to attracting and retaining talent with the skills needed to revolutionise the sector.
One way to do this is through data science. The offshore oil and gas industry can easily use AI to access the data used for oil and gas exploration.
An example of AI adoption in the oil and gas industry is BP’s investment in Belmont Technology in 2019. BP made the move to work with the technology start-up to bolster its AI capabilities, developing a cloud-based platform nicknamed “Sandy”.
The platform enabled BP to derive actionable insights from geophysics, geology, historic and reservoir project information. BP could then consult the data using neural networks to interpret simulation results.
AI skills in-demand
We've here for you a snapshot of the evolving skill requirements in the oil and gas industry, focusing on the impact of AI.
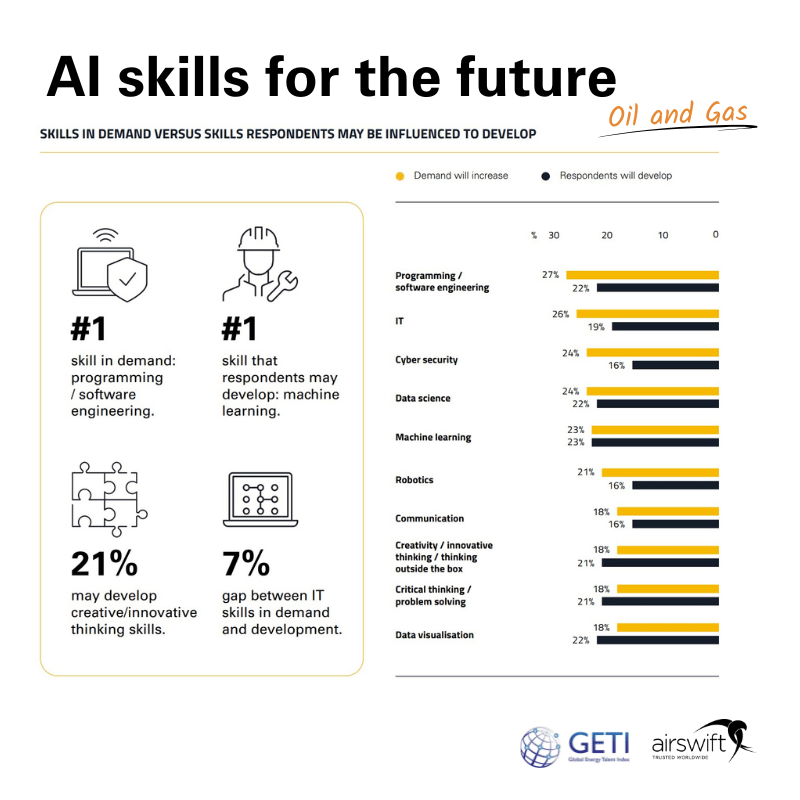
Programming/software engineering emerges as the top skill in demand, paralleled by its perceived necessity for future development.
The demand for cyber security skills (24%) slightly outpaces the intent to develop them (16%), underscoring the importance of security in an increasingly digital sector.
Similarly, while there’s a strong demand for data science and machine learning skills, the willingness to develop these skills is moderately lower, which could suggest either a current skills deficit or a hesitation to engage with these technologies.
You can find more insights like that in our latest GETI report, delving into the transformative impact AI is set to have on the future workforce.
 Renewable energy
Renewable energy
Renewable energy is shaping our future as governments worldwide look for new ways to reduce carbon emissions and improve efficiency.
As renewable energy sources become more prevalent in the energy mix, it’s becoming more and more critical to predict capacity levels to ensure stable grids.
However, we are witnessing a decrease in generation from older sources like coal, which is responsible for grid inertia due to heavy rotating equipment such as steam turbines. With no grid inertia, we risk less stable power grids, thus making them more prone to power cuts.
AI provides a deeper understanding of these risks using real-time data collected by sensor technologies and satellite imagery. AI can then predict downtime periods and capacity levels, allowing the company to act accordingly.
AI skills in-demand
Our GETI chart present a clear picture of the current and future landscape for skills in-demand in the renewables sector, now heavily influenced by advancements in AI and machine learning.
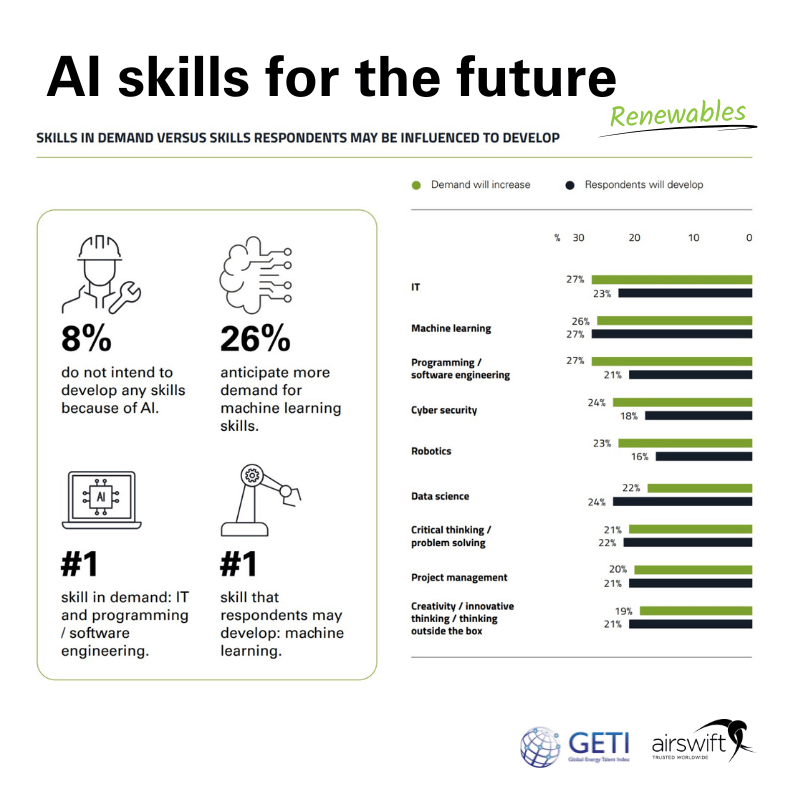
Notably, 8% of respondents do not plan to develop any new skills due to AI, suggesting a degree of reluctance or confidence in their current skill set.
In contrast, 26% anticipate a growing demand for machine learning skills, indicating a significant shift toward these competencies.
IT and programming/software engineering are identified as the most in-demand skills, reflecting the influence of digital transformation across industries.
Additionally, the chart juxtaposes the expected increase in demand for various skills against the proportion of respondents willing to develop them, with IT (27%), machine learning (26%), and programming/software engineering (27%) topping the demand charts.
 Mining
Mining
The mining industry increasingly uses AI to optimise processes, improve safety, enhance decision-making, and derive value from data.
One way mining companies are using AI is to learn more about the environment. AI can map out and predict terrain more accurately than a human, preventing potential errors.
AI is also being used to identify new areas to mine through computer vision systems, pattern matching and predictive data analytics. These allow mining professionals to analyse large amounts of data to predict where to find the best resources.
 Engineering
Engineering
Engineers have a lot of work to carry out across a range of industries. They can use AI to free up their time from working on low-value tasks. Machine learning algorithms help them to discover patterns to make accurate judgments in the long run.
As machines become more sophisticated, they can support manufacturing tasks, production lines. Vehicle engineers have been using robotics on the production line to handle precise moves without human intervention.
AI also helps to break down silos between departments and helps to manage data effectively.
 Software engineering
Software engineering
Human developers need to work on various processes and apply AI at every stage of the software development cycle. It has the tools to transform human language into code and machine language, automatically offering accurate results.
AI algorithms provide intelligent software analysis, testing, development and decision support systems. These tools can support existing software development processes constructed for human-intensive software development.

Source: iStock/alvarez
 Process/chemicals
Process/chemicals
AI has helped the chemicals industry increase operational efficiency, reduce costs, and improve the customer experience. Chemical engineering fields apply it for modelling, classification, process control, fault detection, and diagnosis.
Artificial intelligence can be applied to early product development stages to increase innovation. For example, it can improve research productivity by enabling access to previous relevant data during the initial design stage.
It also enables optimisation at each value chain stage and offers the objective base for value extraction.
AI skills in-demand
The data presented in our GETI chart offers insights into the perceived gaps between the current skills in demand and the skills that individuals in the petrochemical industry plan to develop in light of the growing significance of AI.
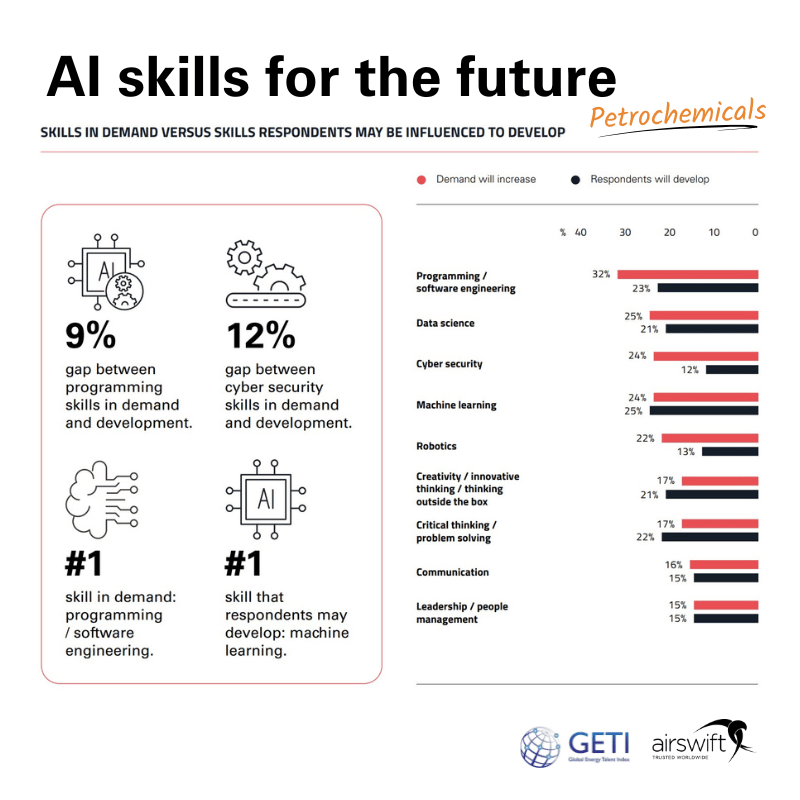
Programming/software engineering retains its position as the most in-demand skill, yet there exists a 9% gap in the industry's programming skills demand and the development intentions of professionals. This indicates an opportunity for increased training and education in this area.
The data shows a strong demand for data science and machine learning skills, reflecting the industry's trend towards data-driven decision-making and automation.
Interestingly, while there is a high perceived increase in demand for these skills, the willingness to develop them lags slightly behind, suggesting potential barriers to upskilling.
 Manufacturing
Manufacturing
60% of manufacturing companies have adopted AI and machine learning models. What’s more, according to Global AI in Manufacturing Market Trends, the market is predicted to reach $16.7 billion by 2026.
One company that has harnessed AI within the manufacturing process is General Electric. The 125-year-old energy firm has begun to include AI throughout all its operations.
 Medical technology
Medical technology
Healthcare AI has seen a rapid increase over the past year. 90% of hospitals now have an AI strategy in place, compared with 2019 when 47% had no process in place.
What’s more, 75% of healthcare executives believe that AI initiatives are even more important now due to the pandemic.
AI has many use cases for the healthcare industry, including the potential to detect dementia before symptoms even appear. A team at the University of Cambridge and the Alan Turing Institute have developed machine learning tools that can spot dementia in patients at a very early stage.
The technology uses brain scans from patients who developed dementia, with machine learning able to detect structural changes in the brain. This, combined with the results from memory tests, generated a prognostic score that revealed the likelihood of the patient having Alzheimer’s disease.
At present, there are very few drugs available to help treat dementia. Still, this ability to identify individuals at the earliest possible stage could allow researchers to develop new medicines that could be tested before the patient’s symptoms are too severe.
 Fintech
Fintech
Artificial intelligence has a variety of practical uses in fintech and the wider finance field. According to Autonomous Research, AI technology could allow financial services to reduce their operational costs by 22% by 2030.
An example is banks using data to decide whether a client is creditworthy. AI enables institutions to look at customer data and make credit decisions without the risk of over or undercharging.
Another good use case for the fintech industry is fraud detection. Machine learning solutions can react to data in real-time to find patterns and relationships and recognise the fraudulent activity.

Source: iStock/vm
AI is changing the world through digitisation
There are several solutions for using AI to help change the world with the digitised process. For example, AI helps in rural areas to boost access to medical care, also known as telemedicine.
Other use cases include enhancing operational efficiencies in the maritime shipping industry and introducing autonomous vehicles for transportation.
Find niche AI talent with Airswift
Here at Airswift, we have more than 40 years helping business leaders develop their global technology and engineering workforce.
With our unrivalled global presence, we can support you at every stage of the recruitment process to find the best AI talent for your company.
We invite you to speak with our talent specialists today so you can source the best talent to accelerate the digital transformation of your business.


