By
Liz Fiumara & Rob Boyle
July 24, 2023
Updated
September 18, 2024
Planning your global expansion strategy? Try a PESTEL analysis first
Okay, so your domestic business is booming in your home country. And demand is growing in international markets. You are considering how to increase sales for your product or service.
But you are stuck on the finer points of planning an international expansion strategy. How can you plan and make an informed decision?
As a starting point, there are the following areas to understand:
- Potential challenges in the macro environment
- International recruitment and finding local employees
- Understanding tax laws that vary from your home market
- Should you outsource or establish an entity in-country?
For the first point - how can you understand the environmental challenges?
Well, a handy planning tool used in business schools is the PESTEL framework
A PESTEL analysis helps to understand the macro-environmental factors in the strategic business environment. These external factors are the ones that are beyond your control and can be grouped into political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal categories.
We will cover PESTEL and how keeping tabs on these external factors can help you plan and deliver your global expansion. Here are the topics:
- Political factors
- Economic factors
- Social and demographic factors
- Technological factors
- Environmental factors and concerns
- Legal factors and regulatory considerations
- Additional factor – ethical considerations
- Understanding the challenges and still expanding
- Could partnering with a global employment specialist help?
NOTE - The model is also known in various guises as PEST, STEP, STEEPLE and PESTLE. It was originally conceived as ETPS by Harvard professor, Francis Aguilar.
So, how does PESTEL help a company with their overseas expansion plan?
Often used for existing challenges, PESTEL is also helpful for new market research. You could use it with a SWOT analysis to identify existing opportunities and potential threats.
Or it can forecast future issues that will need careful management.
A PESTEL analysis will uncover obstacles that will make it harder to do business in a foreign market
Expanding globally carries many challenges due to differences between locations and countries. From language and customs to the pace of business change to the currency or the state of digital technology.
Often, the biggest obstacle to doing business is registering a legal entity in-country. This process can be costly and take up to a year to complete. This time will be better spent growing market share but can get eaten up by paperwork and delays.
Growth can be accelerated by working with an Employer of Record company.
They can help you set up quickly without establishing a legal entity in a particular country. That means - speed to market!
Let’s examine how each of the PESTEL framework's external factors can be used to evaluate the external environment and some questions to ask when planning.
Political factors relating to government influence on the economy
 To what extent does the government intervene in the economy?
To what extent does the government intervene in the economy?- Are there tax policies that can impact businesses and organisations?
- Is their political stability?
- Are there trade tariffs that will be a barrier to doing business?
- Are there any sanctions imposed on the country?
- Are there upcoming elections that could change the attractiveness of the country?
- How quickly are business applications processed? Is it liable to bureaucracy?
For example, if you were looking to start a small business in Asia, the length of time can vary widely
This variance can slow your growth if you are caught unaware.
Airswift can help you establish a presence in Singapore within days. But we know in The Philippines it will take several weeks and perhaps months. In either location, we can have talent deployed and effective immediately through our employer of record model.
The variations in establishment time are huge differences. And if you need to be generating cash quickly, every extra day matters.
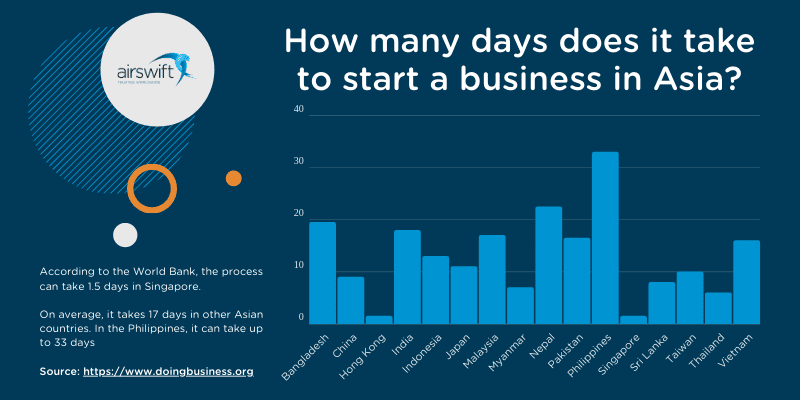
Figure 1: How many days does it take to start a business in Asia? (The World Bank Doing Business Report)
Economic factors affecting business operations when expanding internationally
 What is the economic growth rate? Is there projected growth in GDP over the next 5, 10 and 20 years?
What is the economic growth rate? Is there projected growth in GDP over the next 5, 10 and 20 years?- Are there strategic industries that you can either compete in or supply to?
- For B2C firms, is consumer spending expected to increase? A good indicator would be increasing proportions of middle-class incomes in society.
- What is the unemployment rate?
- Are interest/inflation/foreign exchange rates volatile? Are you capable of managing global payments in this country?
- Are there incentives or foreign direct investment (FDI) initiatives to attract multinationals?
Failing to factor in hidden costs can impact the profitability of your expansion. You need to expect a stable investment plan to continue growing
But volatile inflation rates or exchange rates will erode profits. As business expenses increase you may need to put off investment or hiring decisions.
Using BIS data, we tracked how much a currency had appreciated or depreciated since 2010.
The chart represents how much the rate has deviated up or down each quarter over the 10-year period. The bar for each economy demonstrates how widely the currency had swung from high to low over time.
The currencies of Singapore, New Zealand and the Euro Area did not deviate much. However, there were big swings in Argentina and Russia as economic issues derailed growth. Depending on your business model, this volatility can represent a huge risk.
Of course, it is worth paraphrasing financial advisers and saying...
'Past performance does not predict future returns'
A better indicator of future potential can be seen in the social factors of an economy. In particular, the potential labour force and demographics can influence an economy.
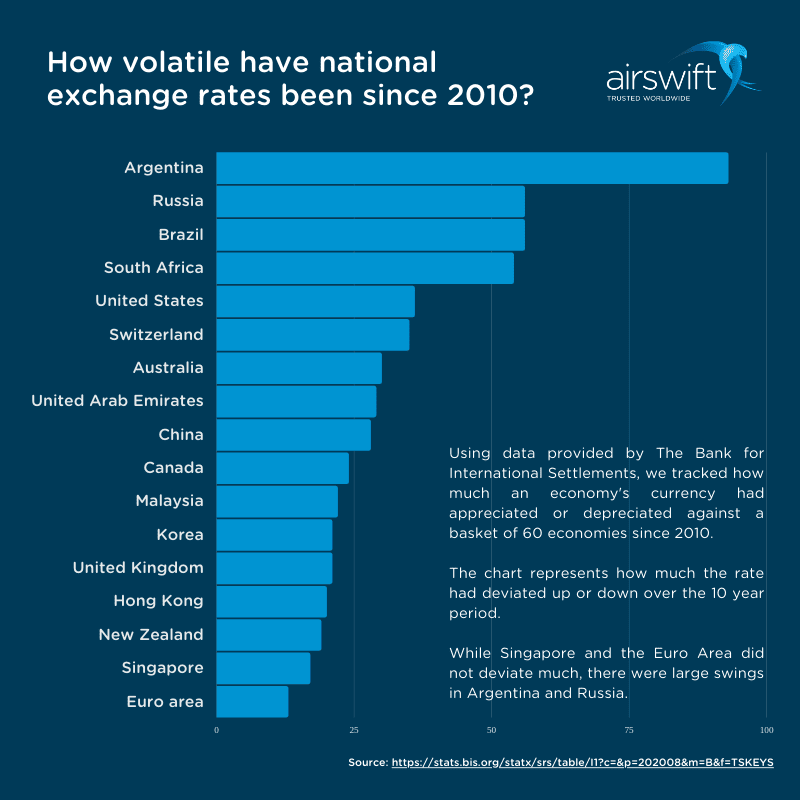
Figure 2: Exchange rate volatility (Bank for International Settlements)
Social and demographic factors impacting business and workforce planning
 Is there enough local talent to meet your needs? If not, are there restrictions on hiring ex-pats?
Is there enough local talent to meet your needs? If not, are there restrictions on hiring ex-pats?- Is the country’s population considered to be young or ageing?
- What are high school graduation rates? How much of the population goes on to earn a degree in higher education?
- What are the sociocultural norms we need to be aware of and how do they impact consumer preferences?
- Is the country stable or is there a history of social unrest?
- Are there religious or cultural factors that you need to be considerate of?
- Is your native language the same as your target country?
- Are there differences in working culture that would be a shock to you or your employees?
If your business will need an educated or large labour force, the social makeup of a country is key. The future availability of talent is paramount to a successful expansion
The rapid expansion of China on the world stage can be attributed to a few factors, including entry into the WTO and gradual economic opening.
Furthermore, a huge driver of economic growth was the availability of a ‘demographic dividend'. They had a high proportion of the population of working age available to industry.
Throughout the latter half of the 20th Century, China had a large working-age population. This was boosted by the migration of talent from agricultural to manufacturing roles.
A large, low-cost labour pool and strategic investment fuelled China’s growth. However, their competitive advantage is reducing as wages, and average ages rise.
Chinese working-age population has peaked and will age over the next 40-50 years.
In comparison, Sub-Saharan African countries like Mozambique has a growing labour pool. India will also maintain a high percentage of working-age civilians over the same period.
This has led to suggestions that India or Africa will be the centre of industry in the mid-21st century.
Alongside reduced availability of workers, an ageing society will have less spending potential. This is a challenge for both government and individuals as social spending and healthcare costs mount.
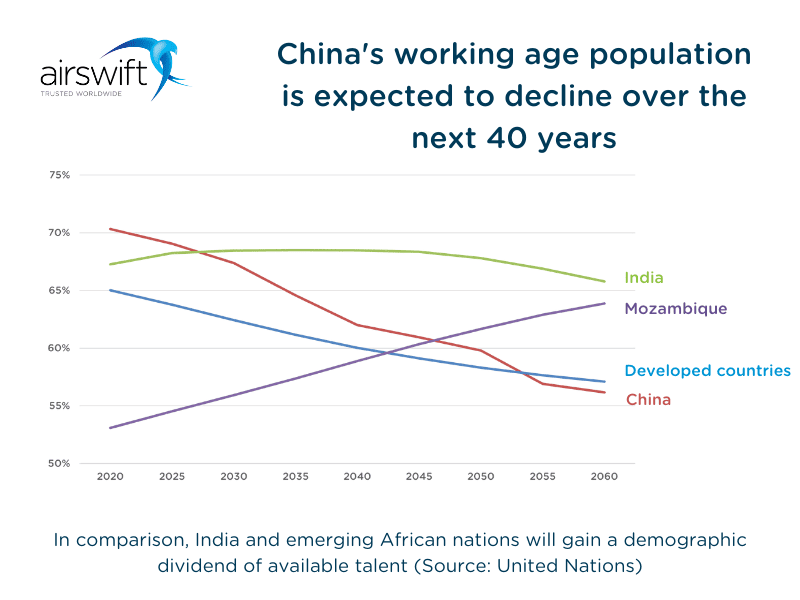
Figure 3: World Population Prospects 2019 (The United Nations)
Technological changes and their impact on international expansion strategies
 Are you able to access tech talent more easily in the new market?
Are you able to access tech talent more easily in the new market?- How can disruptive technologies potentially change the market or industry your business plans to expand to?
- Are there intellectual property considerations?
- Do you have innovative tech that is not available in the new country?
- Are you liable to disruption from local firms protected by domestic laws?
- What government incentives exist to support investment in research & development (R&D)
The availability of a large population is not the only factor to consider. High-technology companies looking to expand may want to consider engineering and technology graduates.
Here, China is successfully managing their economic transition from manufacturing to technology.
China are world leaders in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics undergraduate education.
In fact, they quadrupled the number of STEM graduates between 2000 and 2014. These graduates will now be entering the prime of their careers.
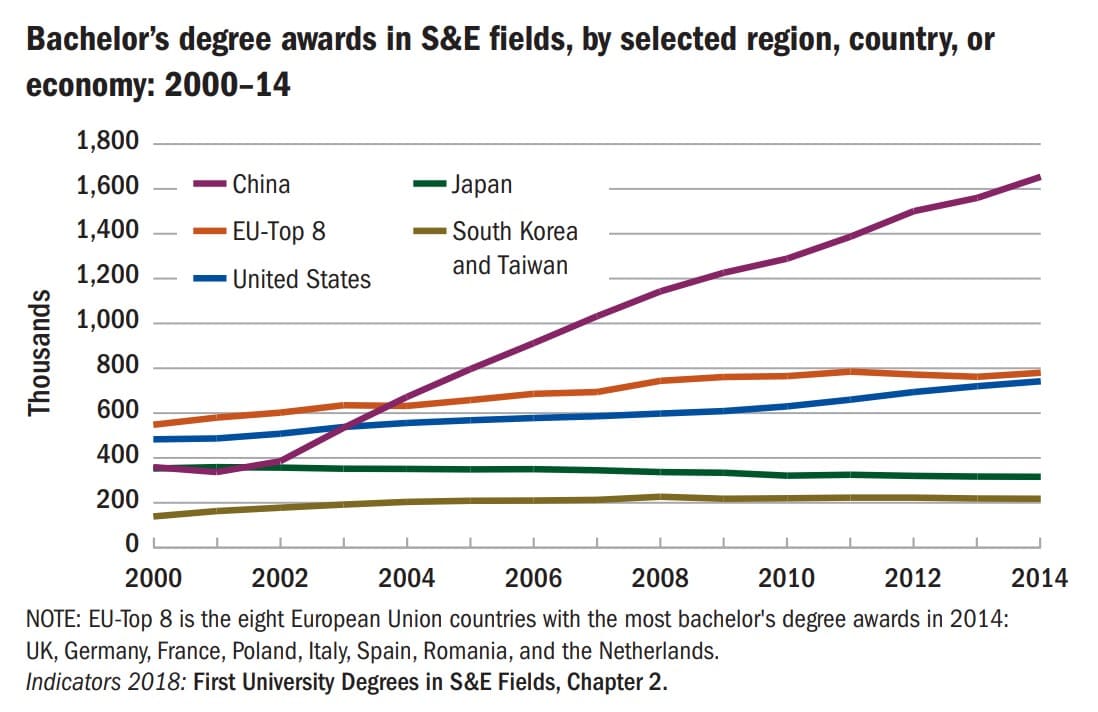
Figure 4: Bachelor's Degree awards in Science & Engineering 2000-2014 (National Science Board)
Spending on research & development can be a good indicator of innovation within a country
Data provided by The World Bank highlights an outlier outside the largest economies. Korea has the highest proportion of researchers per million inhabitants and R&D spend as a share of GDP.
A nation focused on R&D can benefit a business that needs niche talent or an innovative supply chain.
Another innovation indicator is the number of patents filed, and China excels here. By comparison, other BRICS countries (Brazil, Russia, India, and South Africa) are lagging.
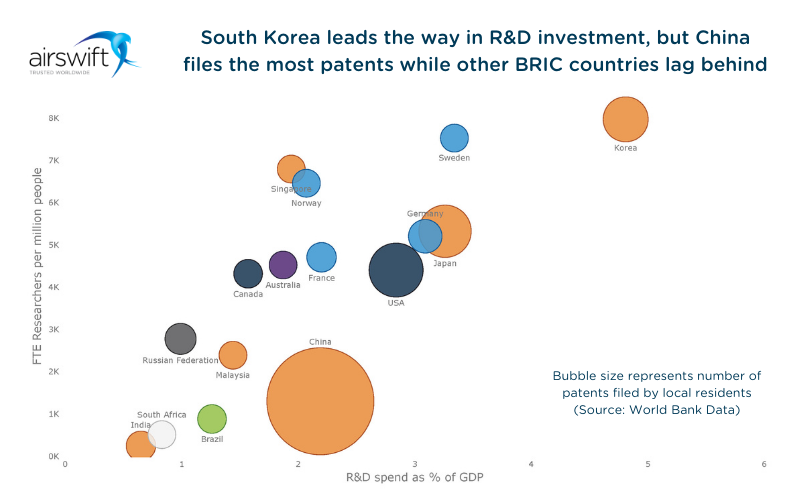
Figure 5: Spending on R&D (as % of GDP) and number of full-time equivalent researchers per million inhabitants (The World Bank)
Environmental regulations and concerns when expanding your business internationally
 Are you compliant with policies relating to power consumption or disposal of hazardous material?
Are you compliant with policies relating to power consumption or disposal of hazardous material?- What impact do carbon footprint targets have on your business?
- Are there extreme weather conditions in the country?
- How quickly and effectively does the local government respond to natural disasters?
- How might natural disasters disrupt local and global supply chains? Would there be alternative supply routes available?
- What is the national policy surrounding energy? Are they investing in renewable energy or oil & gas?
Understanding environmental regulation is essential to maintaining a license to operate in-country
If you were to expand to Europe, you need to be aware of the European Union Emissions Trading System. The EU ETS regulates carbon emissions and can increase business costs.
Implementing processes to ensure EU ETS compliance can be costly. You may need to hire environmental specialists or radically change operational procedures.
Even companies in sectors not regulated by the EU ETS may face a higher cost. Their customers may seek to reduce supply chain spending to mitigate increasing costs.
Local environmental policies will also create opportunities for companies pivoting to meet climate goals.
The UK plans to increase investment in offshore wind and attract global innovation. In fact, IRENA is forecasting global offshore wind capacity to increase 41x by 2050. As the industry grows, a global supply chain will grow with it.
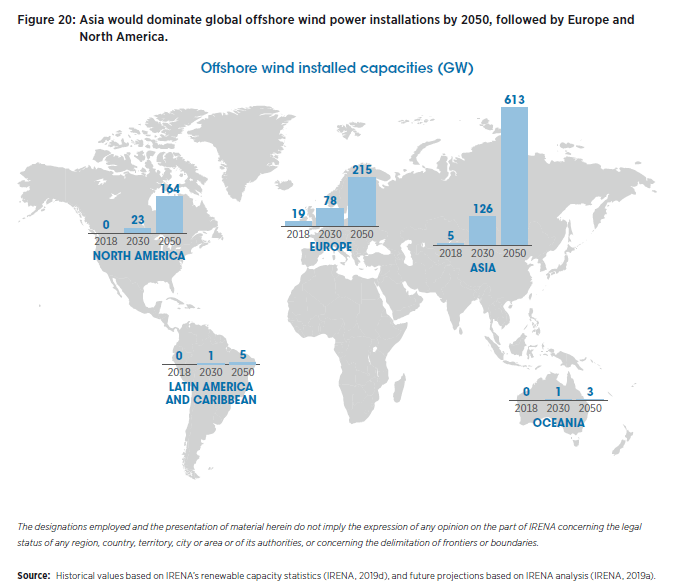
Figure 7: Offshore Wind Installed Capacities (GW) to 2050 (International Renewable Energy Agency - Future of Wind)
Legal and regulatory considerations when expanding your business
 Are there employment laws related to local hiring or immigration restrictions?
Are there employment laws related to local hiring or immigration restrictions?- Do you understand local laws on payroll, taxation, safety, and contracts?
- Do you have a thorough understanding of the termination process for employees?
- What is the taxation policy?
- Are your internal teams equipped to handle regulatory variance in each country?
- How often do employment regulations change?
- What role does the government play in regulations? Is it an interventionist or free market economy?
- Are there competition laws designed to protect local firms against multinationals?
- Can you demonstrate compliance with data protection laws such as GDPR in Europe?
There can be wide variances in regulations across countries
Corporation taxes can vary from 0% in the United Arab Emirates to 40% for foreign companies in India. There are also great differences in dismissal and severance regulations.
Failure to understand labour law can be costly and time-consuming. In the USA, an individual worker dismissed after four years is not entitled to severance or a notice period.
In contrast, a worker in Turkey is entitled to six months’ pay and a two-month notice period.
Mismanaging contracts can also impact your future ability to attract and keep talent. It is advised to work with a local employment expert to guide you throughout your expansion.
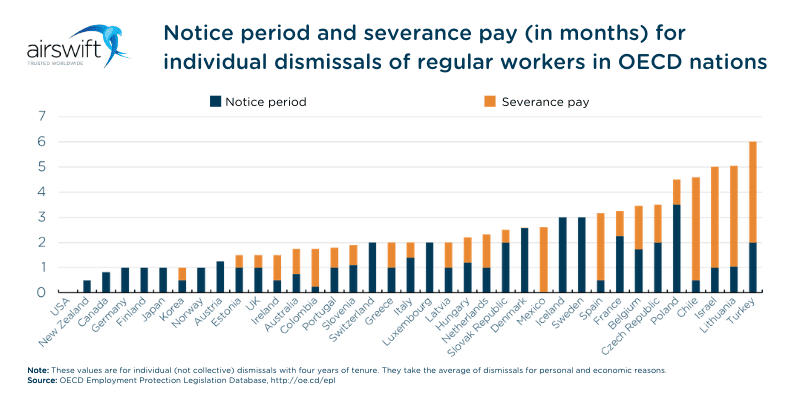
Figure 6: Notice period and severance pay for individual dismissals of regular workers in OECD nations (OECD Employment Protection Legislation Database)
You may have also seen PESTELE with three E’s, with the last E representing ethical factors
In recent years, strategists have added another important factor. Ethical factors should guide business decisions around your workforce and license to operate.
- Does the country have a reputation for poor workforce policies? Does this include child labour or human slavery violations?
- Does the country have policies to encourage fair trade practices?
- Can your business contribute to social improvement through corporate social responsibility initiatives? These could include philanthropic or charitable activity to support national advancement.
Labour laws and workers’ rights vary by country. And not all countries are receptive to a foreign company implementing their local employment policies
If an American company is expanding, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration’s (OSHA) standards may not apply. So, regulating and standardising working conditions between countries will be difficult. This could cause tensions between headquarters and policymakers.
Another ethical factor to consider is expectations of working hours and conditions. Our World in Data found global variance in working hours and productivity levels. An expanding company used to long/short working hours may have a culture shock elsewhere.
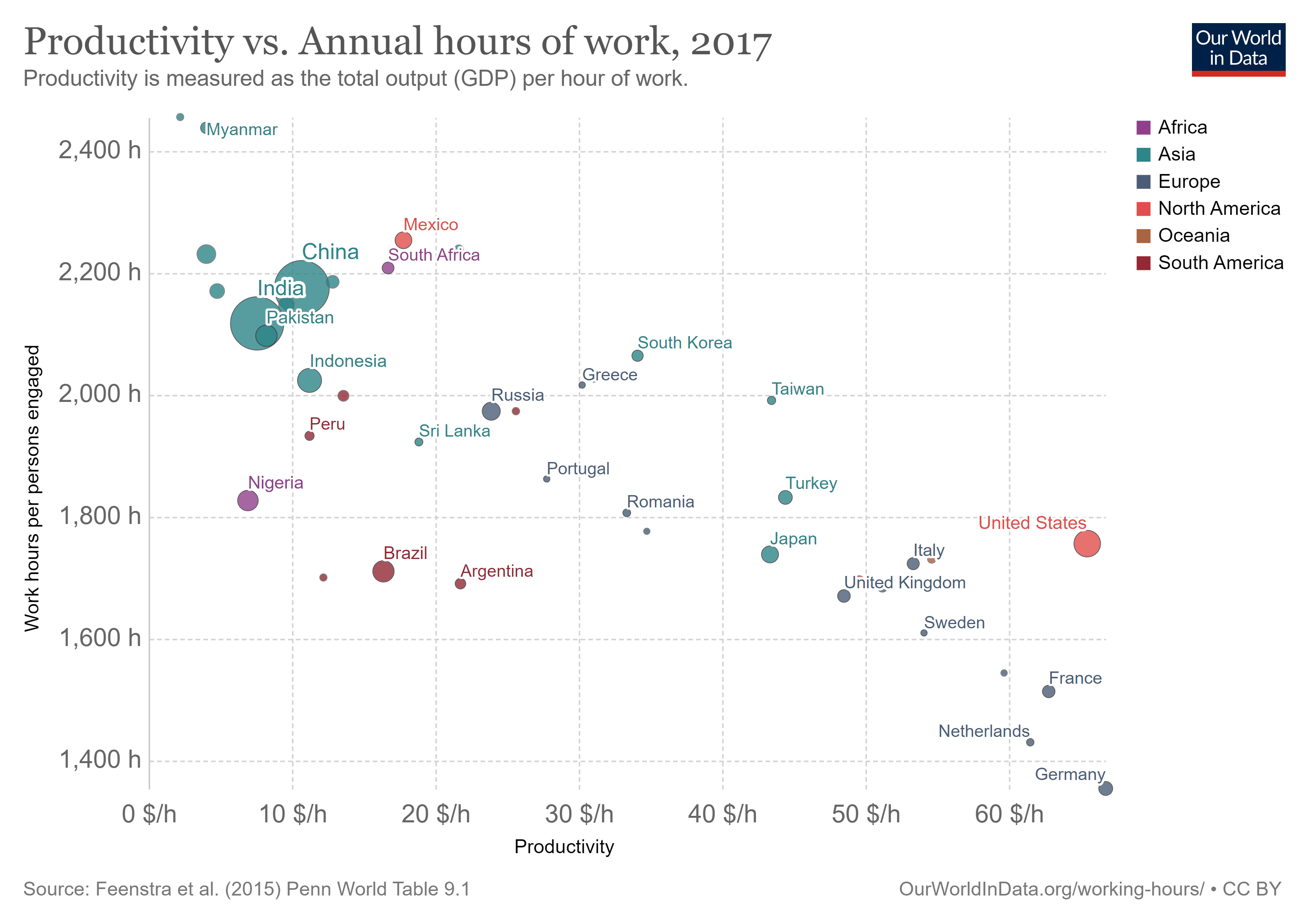
Figure 8: Productivity vs. annual hours of work (Our World in Data)
Okay, so that helps me understand potential constraints. How can I still expand my business overseas?
International growth is key to staying competitive. It’s a process that should be carried out carefully. Otherwise, you may encounter a number of pitfalls.
How partnering with an Employer of Record can help with international expansion.
When planning to expand internationally, it is essential to involve a local expert in your business strategy. Partnering with a global mobility specialist can provide valuable insights and guidance throughout the process, ensuring a smooth and successful expansion.
International companies specialising in Employer of Record services can help navigate the intricacies of expansion.
Here are a few ways how they can do that:
- They have experience operating in the country
- They are familiar with the local employment and tax laws
- They have networks of local talent
- They understand the details of successful and compliant country operations
Here are some of the services they can offer you:
Employer of Record
This is where a provider acts as the Employer of Record. They can act as a third party between the company and its employees. The most important benefit is that the provider holds the legal entity and liability. They also understand how to calculate payroll, taxes, leave accrual and administer benefits.
They are, essentially, a full-scale outsourced Human Resource function for your company, which is beneficial when expanding. Corporate tax liabilities are reduced since they aren’t the legal employer of record, even while technically operating in-country.
Global Immigration Services
If any part of your workforce will include expats, you’ll need to manage immigration service. A local partner can manage work permits, authorisations, applications, and advisory services.
International Payroll
Tax laws vary by location, and payroll is a detailed process that can be prone to error. You may wish to work with a provider with a track record and systems for processing local payroll.
Many companies choose to outsource payroll due to limited infrastructure. They can then save time and money and focus on scaling their operations.
Global Mobility
Mobilizing an expat workforce has many facets. From managing real estate to relocating family members and finding accommodation and schools.
When you work with a Global Mobility provider, they handle this. This then frees you to focus time and attention on setting up an in-country operation.
HR Consulting
When setting up operations in a new location, creating an HR function is essential. As such, you may want to opt for consulting advice from local specialists.
An HR consulting specialist can advise on the following:
- How to set up an entity
- Organisational design
- Implementing in-house payroll functions
- Cost savings and efficiency initiatives
Summing up: using PESTEL analysis to assess risk and sustain growth through international business expansion
When you are growing fast, a market expansion strategy helps you go further and build for the long term. This allows for faster organic growth of a company.
How can a PESTEL analysis help?
A PESTEL analysis identifies the challenges and opportunities of a global expansion. Business leaders can decide if it is a viable opportunity by analysing the new market.
What are the advantages of global expansion?
Global expansion can be a source of new revenue streams and organic growth. It can also help mitigate intense competition through new markets and diversification. Other benefits include improved access to talent pools, investment, and a more diverse customer base.
What are the challenges of international expansion?
A PESTEL analysis uncovers many challenges of global expansion. For business planning, the cultural, political, and legal barriers can be most complex. Key considerations include the following:
- The time and cost of setting up a legal entity
- The risk of tax and labour law non-compliance
- Government policy relating to your industry
- Access to talent
- Cultural barriers
How to execute a successful global expansion strategy
Companies that partner with an Employer of Record service provider find many benefits. The following are benefits that our clients have experienced when partnering with Airswift:
- Local knowledge
- Speed to market
- Cost savings
- Ability to quickly mobilise a global workforce
- Reduction of tax liability


